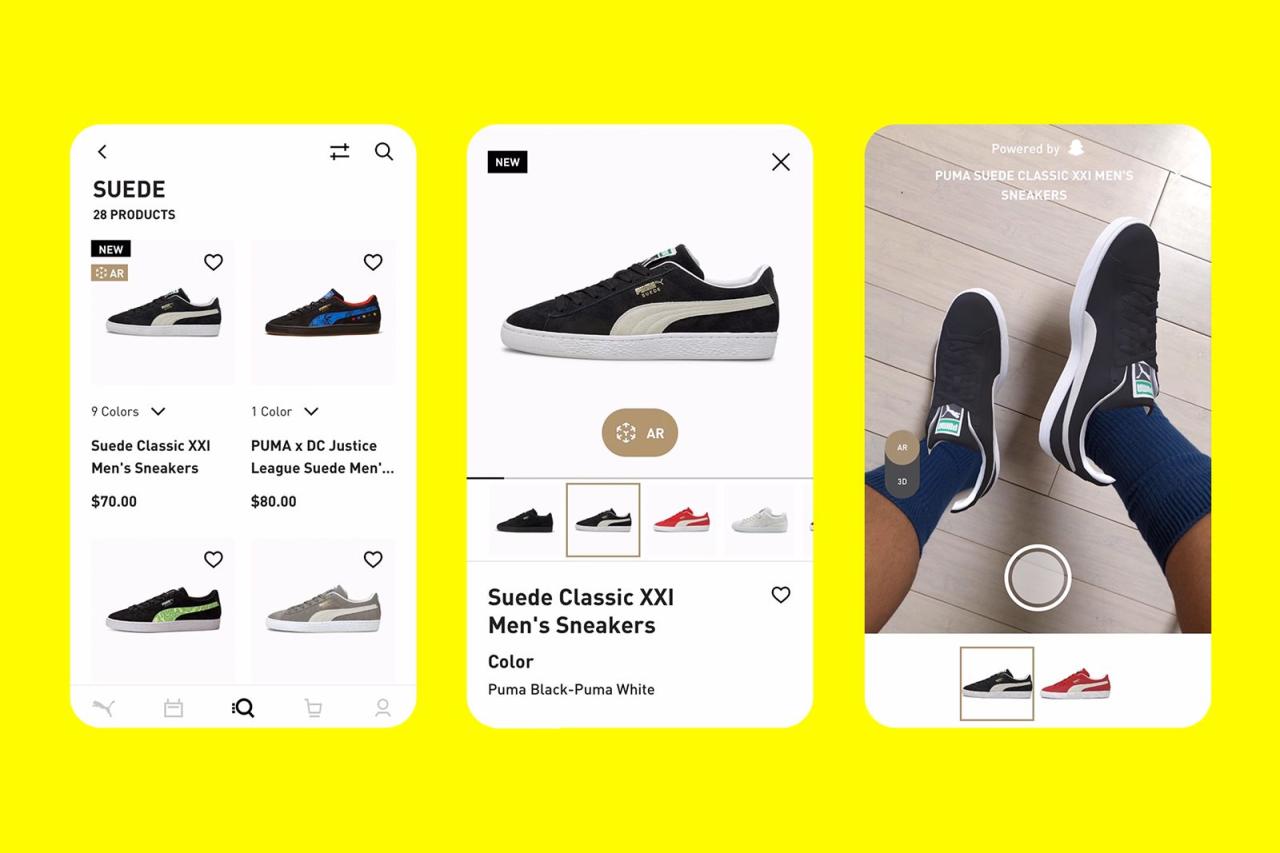
Augmented Reality for Event Planning represents a transformative approach that is reshaping how events are conceptualized and executed. This technology enhances real-world environments with digital overlays, providing planners and attendees alike with immersive experiences that were previously unimaginable. From virtual venue tours to interactive displays, augmented reality offers innovative solutions that elevate event engagement and streamline logistical processes.
The integration of augmented reality in event planning not only captivates participants but also allows organizers to convey complex information in an accessible manner. By leveraging this technology, planners can create memorable events that resonate with audiences, ensuring a unique experience that stands out in a crowded market. The potential of augmented reality is vast, enabling creative storytelling and interactive elements that encourage greater participation.

In recent years, the landscape of technology and its impact on society has evolved dramatically. Specifically, the intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and human interaction presents both opportunities and challenges that warrant careful exploration. This article aims to delve into the multifaceted implications of AI in contemporary society, examining its applications, ethical considerations, and future trajectories.Artificial intelligence, once a concept relegated to the realm of science fiction, has now permeated various sectors, including healthcare, finance, education, and even entertainment.
As organizations increasingly adopt AI-driven solutions, the potential for enhanced efficiency and innovation becomes apparent. For instance, in healthcare, AI algorithms are being used to analyze medical images, predict patient outcomes, and personalize treatment plans. This not only streamlines processes but also improves patient care, showcasing the transformative capabilities of AI.However, the rapid integration of AI raises critical questions regarding ethics and accountability.
As machines take on more decision-making roles, concerns about bias and fairness become prominent. AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate existing societal biases if the data used to train them reflects historical inequities. For example, facial recognition technology has been shown to have higher error rates for individuals from marginalized backgrounds, leading to potential misidentification and discrimination. Therefore, it is essential for developers and policymakers to prioritize fairness in AI design and implementation, ensuring that these technologies serve all segments of society equitably.Moreover, the potential for job displacement due to automation presents another significant challenge.
While AI can enhance productivity, it also poses threats to traditional employment models. According to a report by McKinsey Global Institute, it is estimated that by 2030, up to 375 million workers worldwide may need to switch occupational categories due to the impact of automation. This transition can lead to economic instability and increased inequality if not managed thoughtfully. Consequently, discussions surrounding workforce retraining and the future of work must take center stage in the broader discourse about AI.In addition to employment concerns, the ramifications of AI extend to privacy and surveillance.
The proliferation of AI technologies, particularly in the context of data collection and analysis, raises pertinent questions about individual rights and freedoms. The ability of AI systems to analyze vast amounts of personal data can enhance security measures but also intrude on privacy. Governments and organizations must navigate the delicate balance between leveraging AI for public safety and safeguarding citizens’ rights to privacy.
As such, regulatory frameworks must evolve alongside technological advancements to ensure responsible AI governance.The ethical dimensions of AI also extend to the concept of accountability. When AI systems make decisions—whether in the context of criminal justice, hiring processes, or medical diagnoses—who is held accountable for the outcomes they produce? The lack of transparency in many AI algorithms complicates this issue, as users may not understand the underlying mechanisms that inform decision-making.
As AI becomes more autonomous, establishing clear lines of accountability will be crucial in fostering public trust and promoting ethical standards.Furthermore, the phenomenon of “algorithmic empathy” must be examined in the context of human-AI interaction. AI systems are increasingly designed to mimic human emotional responses, leading to questions about the authenticity of these interactions. For instance, chatbots that provide customer service may simulate empathy, but do they genuinely understand human emotions?
The implications of relying on AI for emotional support or companionship raise complex ethical questions about the nature of relationships and the human experience.As AI continues to evolve, its potential applications are limited only by the boundaries of innovation and imagination. In the realm of education, for example, AI-powered platforms can tailor learning experiences to individual student needs, promoting personalized education at scale.
By analyzing data on student performance and engagement, these systems can adapt curricula in real-time, providing targeted interventions that enhance learning outcomes. This shift towards personalized education signifies a transformative movement that may redefine traditional pedagogical approaches.Moreover, in the field of climate change, AI technologies are being leveraged to decipher complex data patterns and develop predictive models that inform policy decisions.
From optimizing energy consumption to enhancing disaster response strategies, AI has the potential to play a pivotal role in addressing some of the most pressing global challenges. However, the integration of AI in environmental contexts requires careful consideration of sustainability and ethical implications, ensuring that technological advancements align with ecological stewardship.Looking ahead, the future trajectory of AI will depend on collaborative efforts among stakeholders.
Researchers, technologists, policymakers, and civil society must engage in dialogue to shape a vision for AI that prioritizes human welfare and ethical integrity. This collaborative approach will be essential in addressing the myriad challenges posed by AI, while also harnessing its transformative potential for positive societal impact.In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence into various aspects of life holds immense promise but also entails significant challenges.
As society navigates this uncharted territory, it is imperative to foster a nuanced understanding of AI’s implications, emphasizing ethical considerations, accountability, and inclusivity. The journey towards a future where AI coexists harmoniously with human values will require collective vigilance, thoughtful discourse, and proactive policymaking. By prioritizing these elements, society can harness the potential of AI while mitigating its risks, ultimately paving the way for a more equitable and just world.